Oral Cancer Screening
Oral Cancer Screening - A Vital Part of Dental Examinations
Oral cancer screening is an essential part of dental examinations. It is a routine preventive procedure aimed at early detection of oral cancer or precancerous lesions that could lead to oral cancer. It's crucial for everyone but particularly for those with a high risk of oral cancer.
The Prevalence of Oral Cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, nearly 54,010 new cases of oral cavity or oropharyngeal cancer were estimated to be diagnosed in the United States in 2022, resulting in approximately 10,850 deaths. Globally, oral cancer ranks as the sixth most common cancer and is responsible for many deaths every year. These alarming statistics underscore the importance of routine oral cancer screenings in early detection and timely treatment.
The Necessity of Oral Cancer Screening
Oral cancer often begins as a barely noticeable change in the mouth's tissue or an unhealed sore, which might not be painful initially. By the time the signs and symptoms become evident, the cancer might have already reached an advanced stage. Regular oral cancer screening can help detect these changes or abnormalities early when there's a better chance of curing the disease.
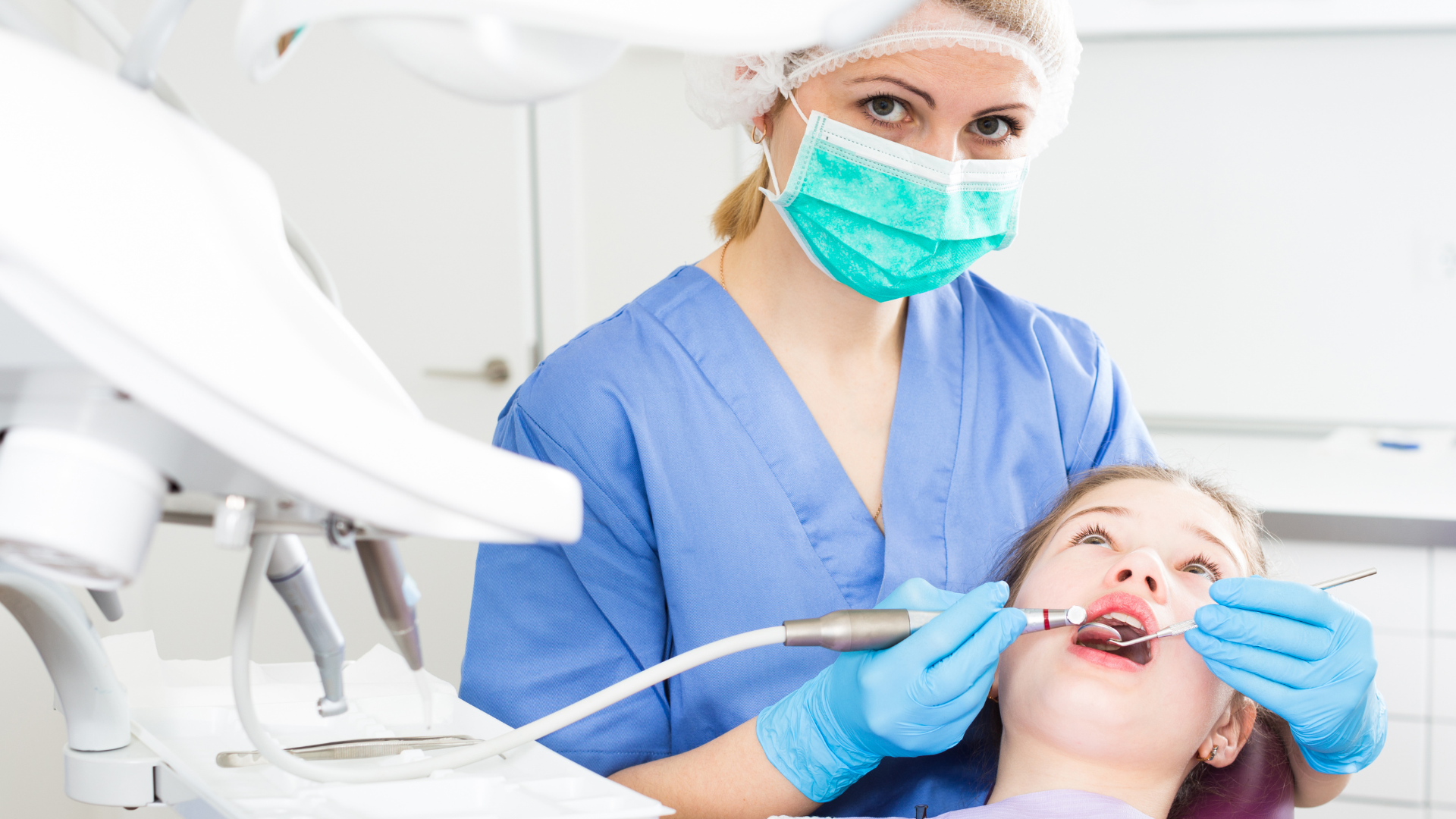
How Oral Cancer Screening is Conducted
Oral cancer screening is quick, painless, and can be completed in just a few minutes during your regular dental check-up. It involves a visual and physical examination of the entire oral cavity, including the lips, cheek lining, gums, front part of your tongue, the floor of the mouth beneath the tongue, and the roof of the mouth. Your dentist will also feel the lymph nodes in your neck and jaw area and may inspect the back of your throat and tonsils.
During the visual exam, your dentist will look for any abnormalities such as sores, white or red patches, swelling, or unusually colored tissue. During the physical exam, your dentist will touch around your jaw, under your chin, and in your oral cavity to feel for any unusual lumps, nodules, or other abnormalities.
Some dentists use additional tests to aid in identifying areas of abnormal cells in the mouth and throat. These might involve using a special dye or light to check for abnormalities not visible to the naked eye.
What the Results Might Mean for Treatment
If your dentist identifies any signs of oral cancer during the screening, they may refer you to a specialist for further diagnostic tests. This might include a biopsy procedure to remove a sample of cells for laboratory testing to determine whether cancer cells are present.
If oral cancer is confirmed, treatment options typically include surgery to remove the cancerous growth, followed by radiation therapy or chemotherapy to kill any remaining cancer cells. Early detection through routine screenings significantly improves the prognosis and reduces the complexity of treatment.
Conclusion
Oral cancer screening is a small investment of time that can potentially save your life. As part of your regular dental check-up, it's a simple step towards ensuring your overall oral health and wellness.